![]()

(The walls from the second storey dropped out during the earthquake.)
The most common damage and the greater amount of
injuries caused by earthquakes is a result of falling objects. Much of the world's
population live in densely populated urban areas which make them particularly vulnerable
to building collapse and being struck by falling objects. Earthquakes can also
topple bridges, towers and dams as well as trigger large landslides. Each of these present
unique problems and can result in floods and fires which may be more devastating than the
direct effects of the earthquake.

(The side wall of a factory collapsed after an earthquake.)
Besides the trembling and shaking of the earth caused by earthquakes, other consequences
can result in tremendous destruction. When shock waves from an earthquake strike some
types of soil, they result in a condition called liquefaction. Liquefaction occurs when
these soils lose their ability to bear weight and behave much like quicksand. Buildings
which have been constructed on these soils quickly topple and may even be swallowed up.
This phenomena was observed in the big earthquake which struck San Francisco in 1906.

Subsea tremors may result in a tsunami. A tsunami is another name for a tidal wave but
because tides have nothing to do with the creation of these waves, the term tsunami is
used instead. These waves move with tremendous speed and
power and can devastate coastal communities where the sea bottom "lifts" the
water as it rolls up on the land.
The pictures below are
some more examples of what the destruction earthquakes had caused.

(The beams of a building buckled after the earthquake.)

(A house fallen down after an earthquake.)

(An earthquake which happened in the past.)
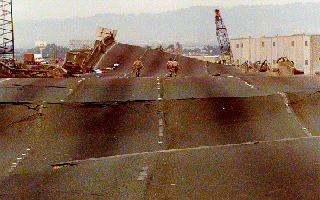
(The bridge is bent due to the earthquake.)

(The debris of a building.)

(A bridge collapsing.)